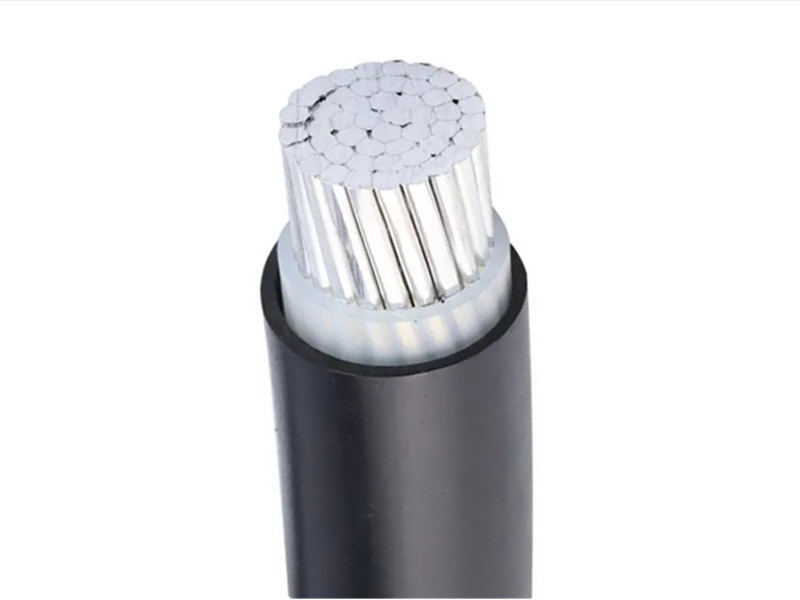
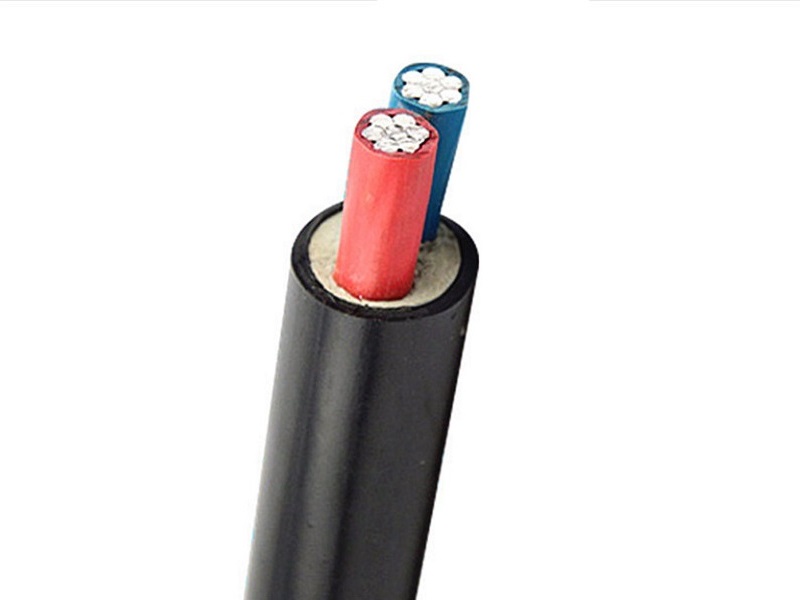
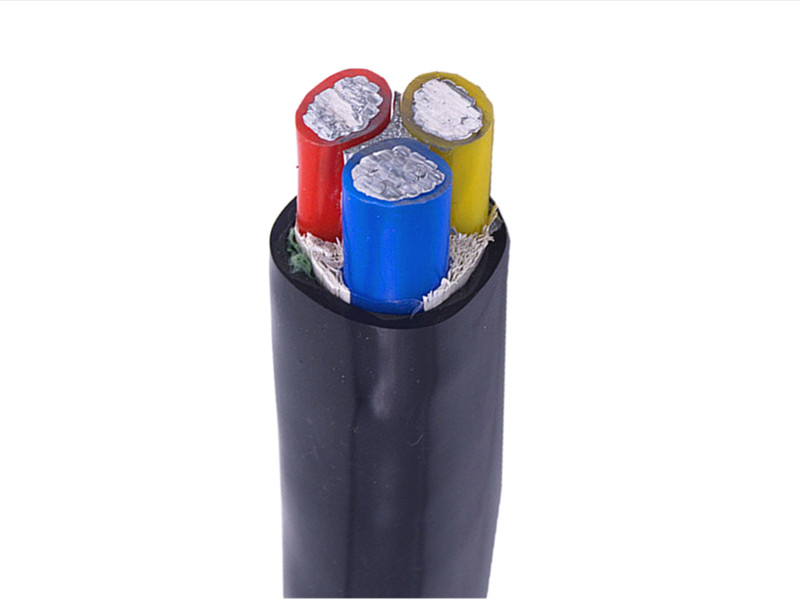
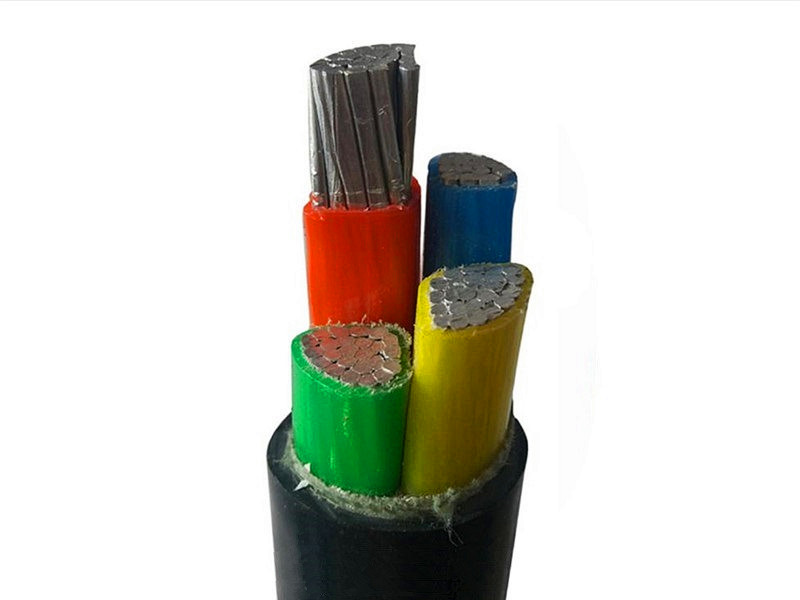
What is a control cable?
PVC insulated and sheathed control cables suitable for industrial and mining enterprises, energy and transportation departments, and for controlling and protecting lines with AC-rated voltage below 450/750 volts.
Features of control cables
1. DC resistance: 20ºC, 0.4mm copper wire, less than or equal to 148Ω/km, 0.5mm copper wire, less than or equal to 95Ω/km.
2. Insulation electric strength: 1min 1kv between conductors without breakdown, 1min 3kv between conductors and shielding without breakdown.
3. Insulation resistance: each core wire is grounded with other cores, the control cable is more excellent than 10000MΩ.km, and the HYAT cable is more fantastic than 3000MΩ.km.
4. Working capacitance: average value 52±2nF/km
5. Far-end crosstalk defense: at 150kHZ, the average power of the specified combination is greater than 69dB/km.
Application of control cables
Applicable to industrial and mining enterprises, energy, and transportation departments. Control cables are moisture-proof, anti-corrosion, and damage-proof and can be laid in tunnels or cable trenches.
The difference between control cables and power cables
1. Different concepts
Power cable: refers to a line with a large wire diameter, generally three or four cores, with thicker insulation between phases and transmitting electric energy. It is used to send and distribute large-function electric energy in the main line of the power system. The rated voltage is generally 0.6/1kV and above. , the current is higher, and the number of cable cores is less.
Control cables: Control cables are used to transmit control signals, with a rated voltage of 450/750V, and directly transfer electric energy from the power distribution point of the power system to the power connection lines of various electrical equipment and appliances. According to the standard, the control cable is 61 cores, but it can also be customized according to user requirements.
2. Different fields of application
Power cables: The cable products used in the power system mainly include bare overhead wires, bus bars (busbars), power cables (plastic cables, oil-paper power cables (basically replaced by plastic power cables), rubber sheathed cables, overhead insulated cables), Branch cables (replacing some busbars), magnet wires, and electrical equipment wires and cables for power equipment, etc.
Control cables: used in computer systems, information transmission systems, robot systems, numerical control equipment systems, automation systems, drag chain systems, etc.
3. Different number of cores
Power cable: the wire diameter is thick, generally three cores or four cores.
Control cable: the number of cores is more. According to the standard, there are 61 cores.
4. Different voltage
Power cables: the rated voltage is generally 0.6/1kV and above.
Control cable: the rated voltage is 450/750V.
5. Different load flow
Power cable: It is used to transmit and distribute large-function electric energy in the main line of the power system, and the current is relatively large.
Control cable: used to transmit control signals and directly transmit electric energy from the power distribution point of the power system to the power connection lines of various electrical equipment.